
Get the latest news, advances in research, policy work, and education program updates from HAI in your inbox weekly.
Sign Up For Latest News
The demand for AI-related professional skills is increasing across virtually every American industrial sector.
Across every sector in the United States for which there is data (with the exception of agriculture, forestry, fishery and hunting), the number of AI-related job postings has increased on average from 1.7% in 2021 to 1.9% in 2022. Employers in the United States are increasingly looking for workers with AI-related skills.

For the first time in the last decade, year-over-year private investment in AI decreased.
Global AI private investment was $91.9 billion in 2022, which represented a 26.7% decrease since 2021. The total number of AI-related funding events as well as the number of newly funded AI companies likewise decreased. Still, during the last decade as a whole, AI investment has significantly increased. In 2022 the amount of private investment in AI was 18 times greater than it was in 2013.

Once again, the United States leads in investment in AI.
The U.S. led the world in terms of total amount of AI private investment. In 2022, the $47.4 billion invested in the U.S. was roughly 3.5 times the amount invested in the next highest country, China ($13.4 billion). The U.S. also continues to lead in terms of total number of newly funded AI companies, seeing 1.9 times more than the European Union and the United Kingdom combined, and 3.4 times more than China.

In 2022, the AI focus area with the most investment was medical and healthcare ($6.1 Billion); followed by data management, processing, and cloud ($5.9 billion); and fintech ($5.5 billion).
However, mirroring the broader trend in AI private investment, most AI focus areas saw less investment in 2022 than in 2021. In the last year, the three largest AI private investment events were: (1) a $2.5 billion funding event for GAC Aion New Energy Automobile, a Chinese manufacturer of electric vehicles; (2) a $1.5 billion Series E funding round for Anduril Industries, a U.S. defense products company that builds technology for military agencies and border surveillance; and (3) a $1.2 billion investment in Celonis, a business-data consulting company based in Germany.

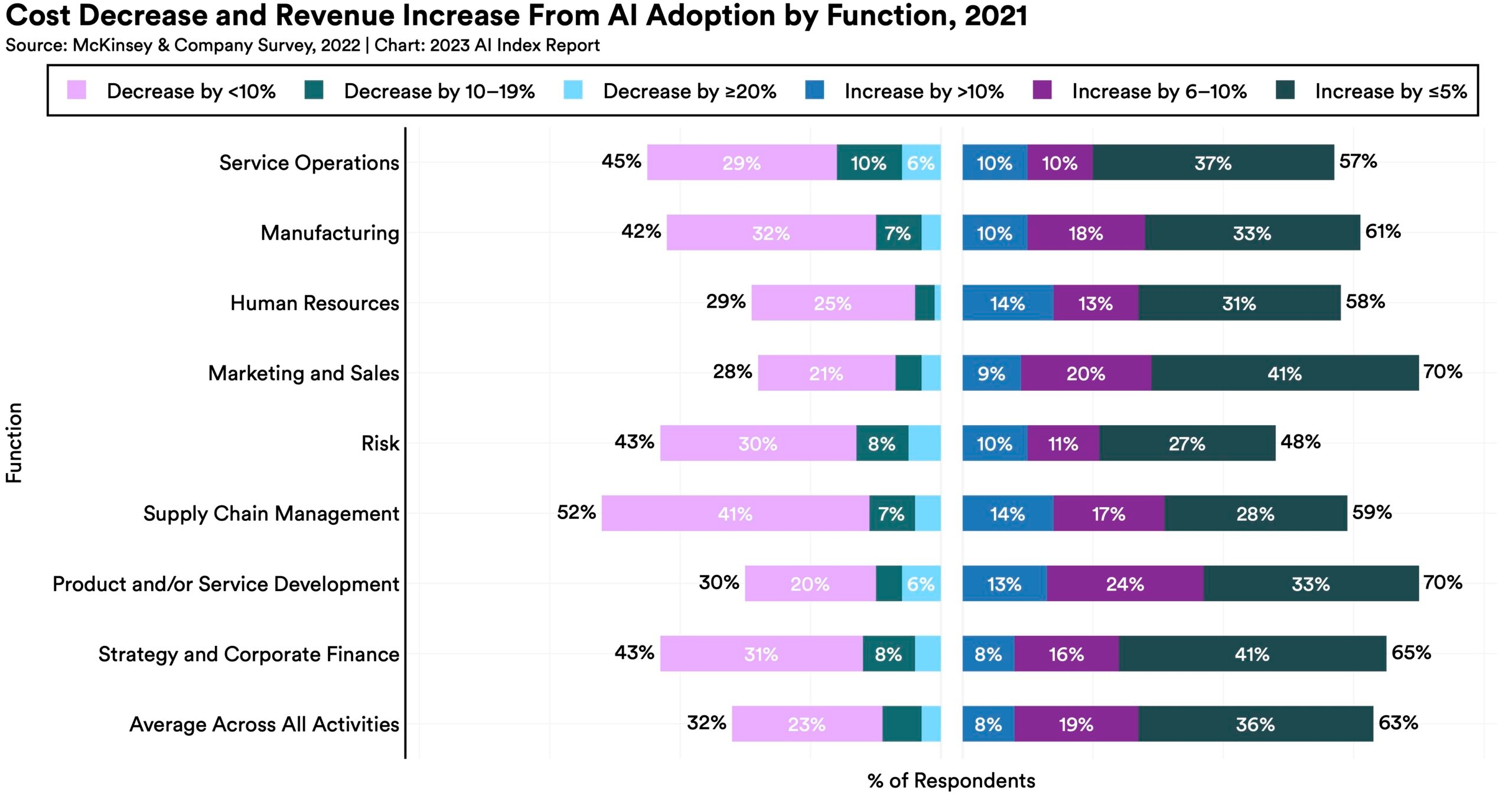
While the proportion of companies adopting AI has plateaued, the companies that have adopted AI continue to pull ahead.
The proportion of companies adopting AI in 2022 has more than doubled since 2017, though it has plateaued in recent years between 50% and 60%, according to the results of McKinsey’s annual research survey. Organizations that have adopted AI report realizing meaningful cost decreases and revenue increases.
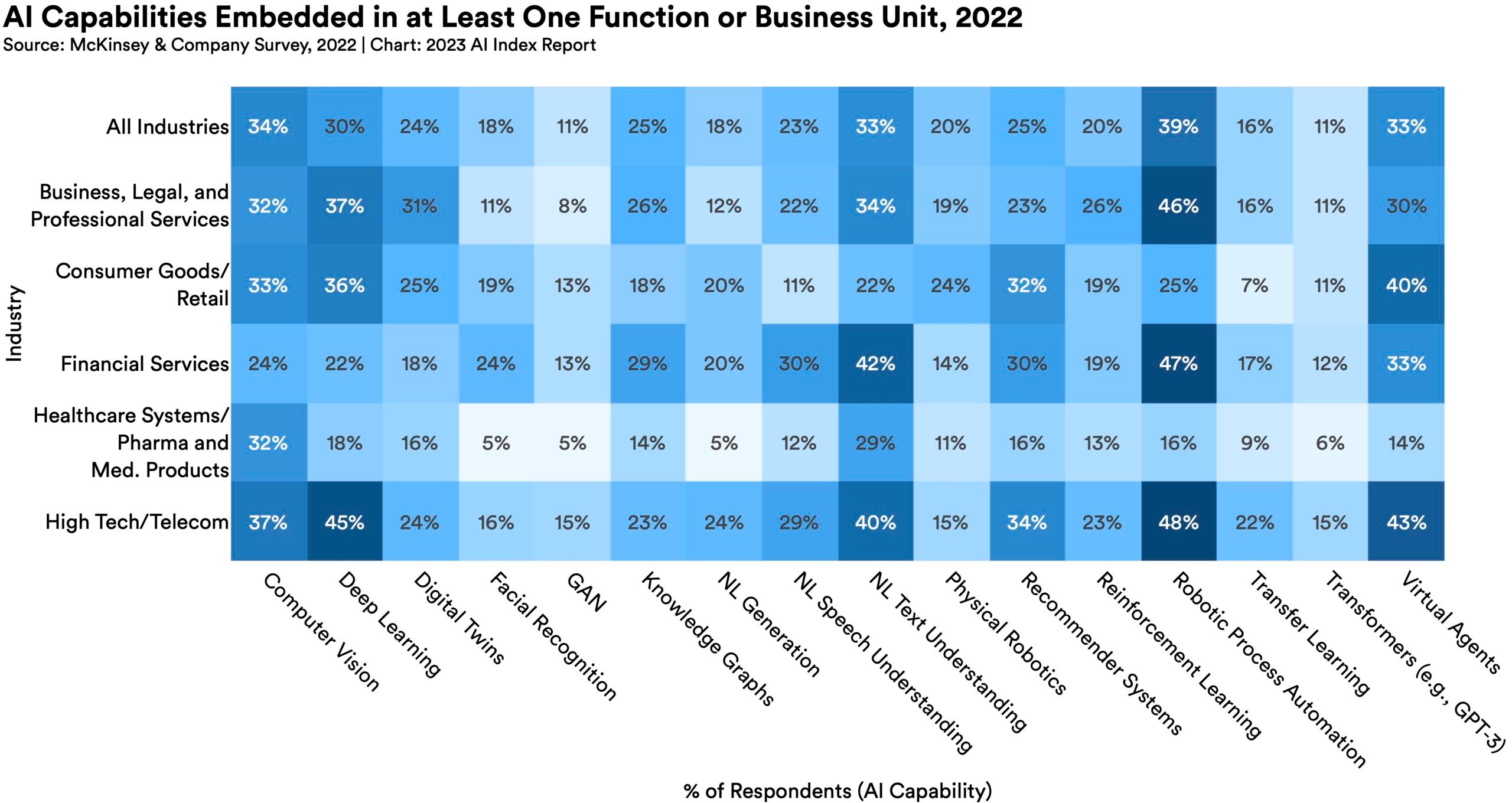
AI is being deployed by businesses in multifaceted ways.
The AI capabilities most likely to have been embedded in businesses include robotic process automation (39%), computer vision (34%), NL text understanding (33%), and virtual agents (33%). Moreover, the most commonly adopted AI use case in 2022 was service operations optimization (24%), followed by the creation of new AI-based products (20%), customer segmentation (19%), customer service analytics (19%), and new AI-based enhancement of products (19%).
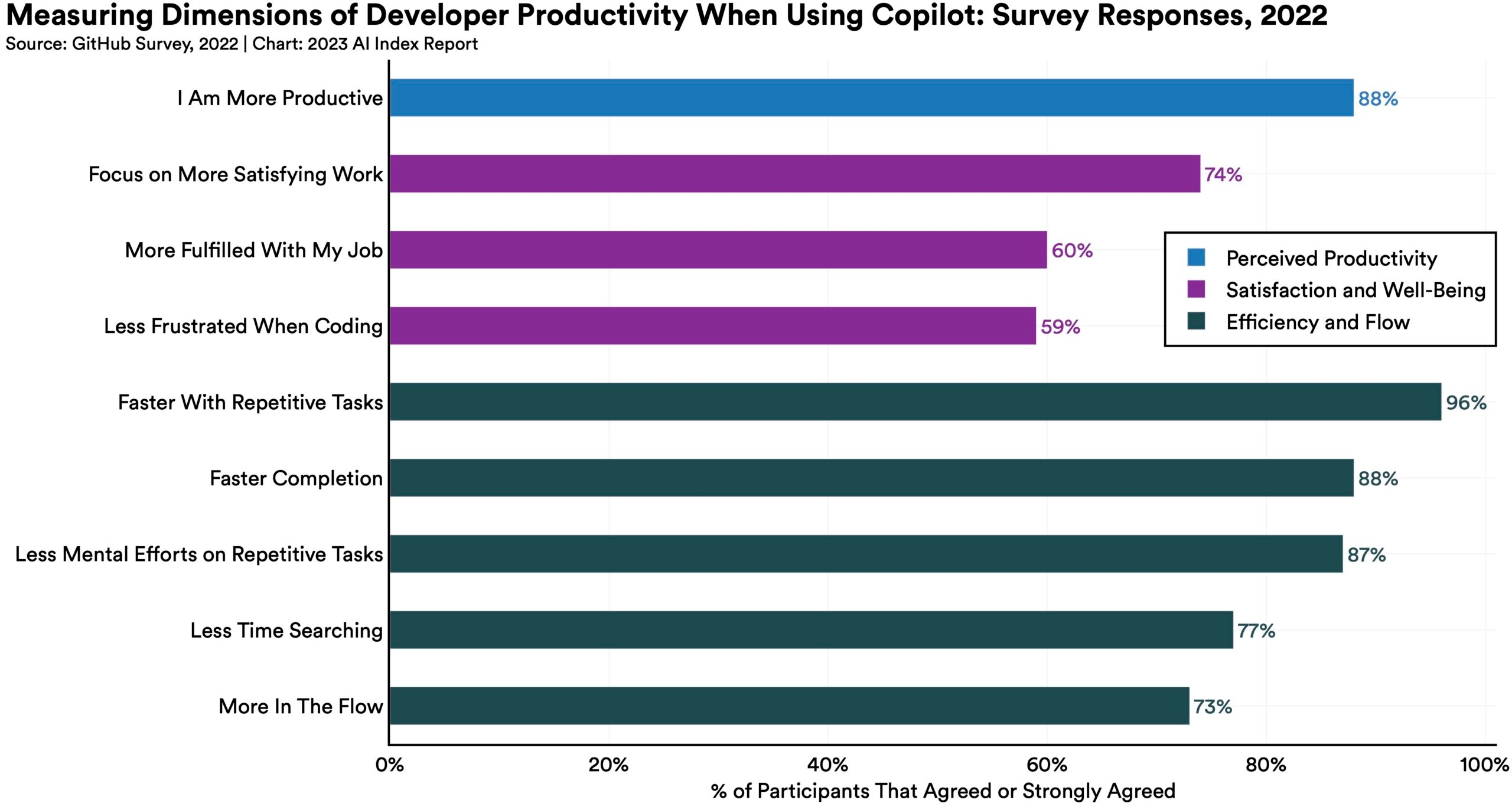
AI tools like Copilot are tangibly helping workers.
Results of a GitHub survey on the use of Copilot, a text-to-code AI system, find that 88% of surveyed respondents feel more productive when using the system, 74% feel they are able to focus on more satisfying work, and 88% feel they are able to complete tasks more quickly.
China dominates industrial robot installations.
In 2013, China overtook Japan as the nation installing the most industrial robots. Since then, the gap between the total number of industrial robots installed by China and the next-nearest nation has widened. In 2021, China installed more industrial robots than the rest of the world combined.
