All Work Published on Generative AI

This brief introduces a generative AI agent architecture that can simulate the attitudes of more than 1,000 real people in response to major social science survey questions.
This brief introduces a generative AI agent architecture that can simulate the attitudes of more than 1,000 real people in response to major social science survey questions.

HAI Policy Fellow Riana Pfefferkorn discusses the policy implications of the "mass digital undressing spree,” where the chatbot Grok responded to user prompts to remove the clothing from images of women and pose them in bikinis and to create "sexualized images of children" and post them on X.
HAI Policy Fellow Riana Pfefferkorn discusses the policy implications of the "mass digital undressing spree,” where the chatbot Grok responded to user prompts to remove the clothing from images of women and pose them in bikinis and to create "sexualized images of children" and post them on X.
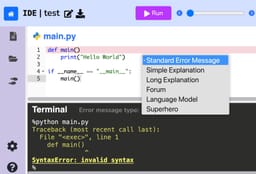
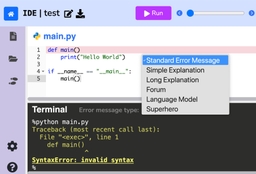
In this paper, we evaluate the most effective error message types through a large-scale randomized controlled trial conducted in an open-access, online introductory computer science course with 8,762 students from 146 countries. We assess existing error message enhancement strategies, as well as two novel approaches of our own: (1) generating error messages using OpenAI's GPT in real time and (2) constructing error messages that incorporate the course discussion forum. By examining students' direct responses to error messages, and their behavior throughout the course, we quantitatively evaluate the immediate and longer term efficacy of different error message types. We find that students using GPT generated error messages repeat an error 23.1% less often in the subsequent attempt, and resolve an error in 34.8% fewer additional attempts, compared to students using standard error messages. We also perform an analysis across various demographics to understand any disparities in the impact of different error message types. Our results find no significant difference in the effectiveness of GPT generated error messages for students from varying socioeconomic and demographic backgrounds. Our findings underscore GPT generated error messages as the most helpful error message type, especially as a universally effective intervention across demographics.
In this paper, we evaluate the most effective error message types through a large-scale randomized controlled trial conducted in an open-access, online introductory computer science course with 8,762 students from 146 countries. We assess existing error message enhancement strategies, as well as two novel approaches of our own: (1) generating error messages using OpenAI's GPT in real time and (2) constructing error messages that incorporate the course discussion forum. By examining students' direct responses to error messages, and their behavior throughout the course, we quantitatively evaluate the immediate and longer term efficacy of different error message types. We find that students using GPT generated error messages repeat an error 23.1% less often in the subsequent attempt, and resolve an error in 34.8% fewer additional attempts, compared to students using standard error messages. We also perform an analysis across various demographics to understand any disparities in the impact of different error message types. Our results find no significant difference in the effectiveness of GPT generated error messages for students from varying socioeconomic and demographic backgrounds. Our findings underscore GPT generated error messages as the most helpful error message type, especially as a universally effective intervention across demographics.

This brief tests a variety of ordinary text prompts to examine how major text-to-image AI models encode a wide range of dangerous biases about demographic groups.
This brief tests a variety of ordinary text prompts to examine how major text-to-image AI models encode a wide range of dangerous biases about demographic groups.

HAI Co-Director James Landay and HAI Senior Fellow Erik Brynjolfsson discuss the impacts of AI in 2025 and the future of AI in 2026.
HAI Co-Director James Landay and HAI Senior Fellow Erik Brynjolfsson discuss the impacts of AI in 2025 and the future of AI in 2026.
How Persuasive Is AI-generated Propaganda?

Can large language models, a form of artificial intelligence (AI), generate persuasive propaganda? We conducted a preregistered survey experiment of US respondents to investigate the persuasiveness of news articles written by foreign propagandists compared to content generated by GPT-3 davinci (a large language model). We found that GPT-3 can create highly persuasive text as measured by participants’ agreement with propaganda theses. We further investigated whether a person fluent in English could improve propaganda persuasiveness. Editing the prompt fed to GPT-3 and/or curating GPT-3’s output made GPT-3 even more persuasive, and, under certain conditions, as persuasive as the original propaganda. Our findings suggest that propagandists could use AI to create convincing content with limited effort.
Can large language models, a form of artificial intelligence (AI), generate persuasive propaganda? We conducted a preregistered survey experiment of US respondents to investigate the persuasiveness of news articles written by foreign propagandists compared to content generated by GPT-3 davinci (a large language model). We found that GPT-3 can create highly persuasive text as measured by participants’ agreement with propaganda theses. We further investigated whether a person fluent in English could improve propaganda persuasiveness. Editing the prompt fed to GPT-3 and/or curating GPT-3’s output made GPT-3 even more persuasive, and, under certain conditions, as persuasive as the original propaganda. Our findings suggest that propagandists could use AI to create convincing content with limited effort.
